“Everything grows by sunlight”. Sunlight contains a variety of light, each of which has a different wavelength, showing a different colour. This is because the light goes deep into the tissue and has different effects on living things.
Harvard Medical School Professor Michael Hamblin has published research articles showing that red light can produce a series of thermal effects, photochemical effects, and other biological reactions. It can also penetrate human tissues up to 30mm or more, directly on the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, and subcutaneous tissue. This is because red light of this kind is not found in other types of light, and is therefore known as the “optical window” of human skin.
How is red light absorbed by the body?
In our body tissues, light is mainly absorbed by proteins, pigments, and other large molecules, as well as water molecules. Since water molecules and haemoglobin in the red light band of the light absorption coefficient are small, photons can be deeply penetrated into the tissues to have the corresponding therapeutic effect. Red light and the human body are the closest to the radiation of electromagnetic waves, and is also known as “the light of life”! It is also known as “the light of life”.
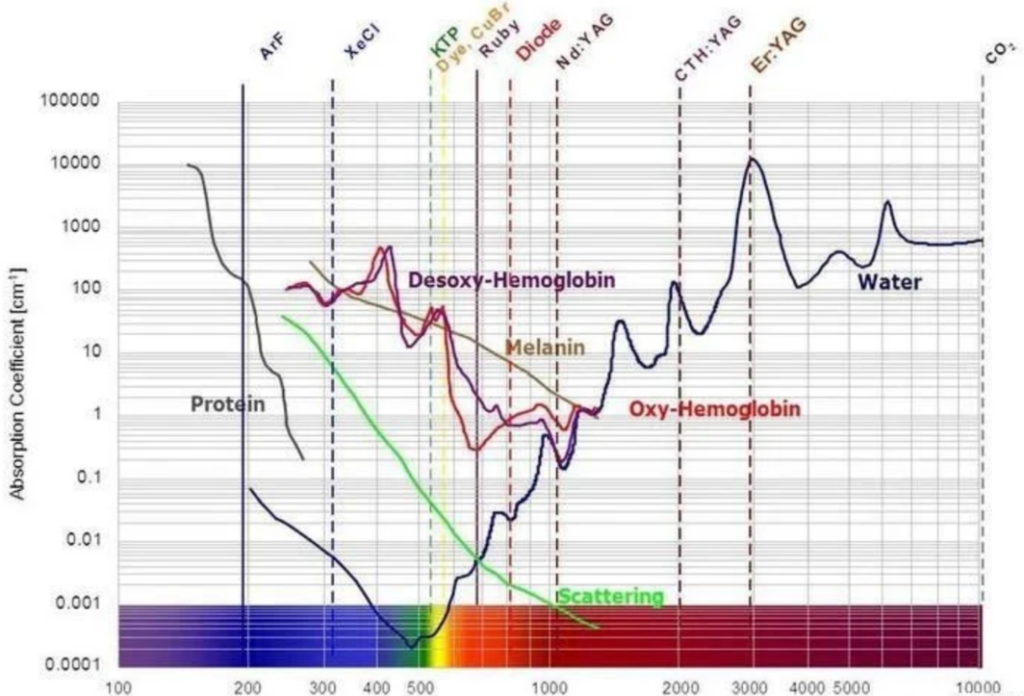
Research Report Chart 2Absorption of different colours of light by skin tissuesIn addition, at the cellular level, mitochondria are the largest absorbers of red light. The red light spectrum is similar to the absorption spectrum of mitochondria, and the photons that are absorbed are introduced into the human body, which results in a very efficient photochemical biological reaction – an enzymatic reaction. This reaction enhances the activity of mitochondrial catalase, superoxide dismutase and other enzymes related to energy metabolism, which accelerates the synthesis of ATP, increases the energy supply of tissue cells and accelerates the process of metabolism and removal of toxic metabolites from the body. It speeds up how the body metabolises and gets rid of toxins.
Mitochondria are the largest absorbers of red light at the cellular level. The red light spectrum is similar to the absorption spectrum of mitochondria, and the photons that are absorbed are introduced into the human body, which results in a very efficient photochemical biological reaction – an enzymatic reaction. This reaction enhances the activity of mitochondrial catalase, superoxide dismutase and other enzymes related to energy metabolism, which accelerates the synthesis of ATP, increases the energy supply of tissue cells and accelerates the process of metabolism and removal of toxic metabolites from the body. It speeds up how the body metabolises and gets rid of toxins.
Another study shows that red light irradiation can change the expression of genes related to sugar, lipid, and protein metabolism, making it easier for fibroblasts to utilize fatty acids as the raw material for synthesizing ATP, thus accelerating the functioning of fats; and at the same time, it can also make the expression of genes related to energy metabolism up-regulated, such as NADH dehydrogenase, ATP synthetase, and electron-transferring flavin proteins, which is conducive to repairing and regenerating damaged tissues, and stimulating nerve tissues to achieve the treatment purpose. It can also stimulate the nerve tissue to achieve the therapeutic purpose.
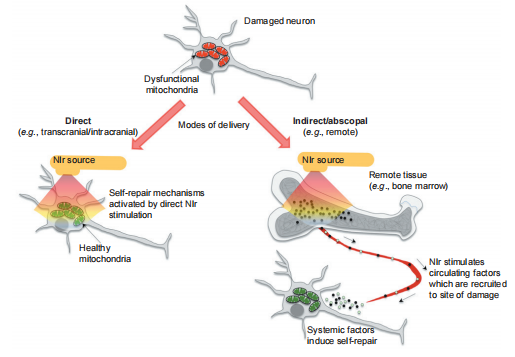
Possible mechanisms of red light-induced neuroprotection
The effects of red light on the human body
There are lots of articles and clinical trials about how red light affects beauty, recovery and immunity. It also plays a key role in promoting the formation of the corpus luteum in the ovary, regulating sex hormone secretion, improving vision, losing weight and fat, and relieving emotions.

Red light can improve skin colour.Other studies have shown that red light can block the action of tyrosinase, which is an enzyme that helps to make skin colour. It can also activate a protein called extracellular regulated protein kinase, which can reduce the production of tyrosinase and other related proteins. This can help to improve skin colour and reduce pigmentation problems, such as spots, acne, and other skin discolouration.
1.Red light effectively improves pigmentation
Red light makes it easier to continue exercising even when tired.Researchers have found that red light for 20 minutes can improve blood oxygen levels and reduce the body’s use of anaerobic energy production, which leads to less lactic acid build-up during exercise. This can significantly reduce feelings of fatigue and improve the body’s ability to resist fatigue and endurance.
2.Red light improves resistance to fatigue
Red light can also help with vision loss.A study by British scientists in the journal Scientific Reports found that being exposed to deep red light for just three minutes a day can significantly reduce vision loss, with their vision improving by an average of 17 percent.
